Intext Questions
Question 1: Each of these cartoons represents a challenge to democracy. Please describe what that challenge is. Also place it in one of the three categories mentioned in the first section.
A)

Answer: This represents the influence of the rich and powerful people on the election, the basic procedure of democracy.
Challenge – Deepening of democracy.
B)
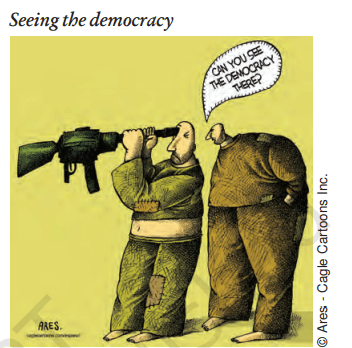
Answer: This represents the existence of non-democratic regimes in the world. It tries to show that democracy does not come by the use of bullet.
Challenge : Foundational challenge.
C)

Answer: This represents that in principle, we talk about gender equality, but in practice male dominancy is observed in democracy.
Challenge – Challenge of expansion.
D)

Answer: This represents how the money is used to influence decision making in democracy by the rich and powerful people.
Challenge – Deepening of democracy.
Question 2: In the following cases and context (as given in the Textbook page 104) give description of the challenges for democracy in that situation.
Answer:
| Case and Context | FeaturesYour description of the challenges for democracy in that situation |
|---|---|
| Mexico: Second free election after the defeat of PRI in 2000; defeated candidates allege rigging. | Challenge of Deepening of democracy –To hold free and fair elections without any malpractices. |
| China: The Communist party adopts economic reforms but maintains a monopoly over political power. | Challenge of Deepening of democracy – To hold multiparty free and fair elections. |
| Pakistan: General Musharraf holds referendum, allegations of fraud in the voter’s list. | Foundational challenge – To eliminate fraud malpractices during referendum and elections. |
| Iraq: Widespread sectarian violence as the new government fails to establish its authority. | Challenge of Deepening of democracy – To prevent the killings based on sects. |
| South Africa: Mandela retires from active politics; pressure on his successor Mbeki to withdraw some concessions given to the white minority. | Challenge of Deepening of democracy – To prevent the domination of the majority community over the minority community. |
| US, Guantanamo Bay: UN Secretary General calls this a violation of international law; US refused to respond. | Foundational Challenge – To prevent the domination of the world body like UNO from domination of influential, rich and powerful countries like the USA. |
| Saudi Arabia: Women were not allowed to take part in public activities, no freedom of religion for the minority. | Challenge of Expansion of democracy – To establish the principle of universal adult franchise and the freedom to practice one’s own religion. |
| Yugoslavia: Ethnic tension between Serbs and Albanians on the rise in the province of Kosovo; Yugoslavia disintegrated. | Challenge of Expansion of democracy – To minimize social differences and divisions and to establish the principle of power sharing. |
| Belgium: One round of constitutional change taken place, but the Dutch speakers not satisfied; they want more autonomy. | Challenge of Deepening of democracy – To give equal political rights to both the Dutch and French speaking communities. |
| Sri Lanka: Peace talks between the government and LTTE breaks down, renewed violence. | Challenge of Expansion of democracy – To adopt federal principles and prevent the brutal state supported violence on the sectarian minority community. |
| US, Civil Rights: Blacks have won equal rights, but they are still poor, less educated and marginalised. | Challenge of Deepening of democracy – To establish economic equality and provide equal opportunities of education and health facilities to all including blacks. |
| Northern Ireland: The civil war has ended but Catholics and Protestants yet to develop trust. | Challenge of Expansion of democracy – To provide equal political, religious and economic freedom to both the communities. |
| Nepal: Constituent Assembly about to be elected; unrest in Terai areas; Maoists have not surrendered arms. | Foundational Challenge – To establish and strengthen democracy and to prevent violence that can threaten the forces of democracy. |
| Bolivia: Morales, a supporter of water struggle, becomes the Prime Minister, MNC’s threaten to leave the country. | Challenge of Deepening of democracy – To establish democratic principles, which are beneficial to each and every section of society. |
Do you need help with your Homework? Are you preparing for Exams?
Study without Internet (Offline)
Question 3: Now that you have noted down all these challenges, let us group these together into some broad categories. Given below are some spheres or sites of democratic politics. You may place against each of these the specific challenges that you noted for one or more countries or cartoons in the previous section. In addition to that write one item for India for each of these spheres. In case you find that some challenges do not fit into any of the categories given below, you can create new categories and put some items under that.
Answer:
| Constitutional design | It is related to framing of the constitution and giving rights and freedom to people. e.g. Saudi Arabia, China, Belgium, Iraq, Myanmar. |
| Democratic rights | To provide people with basic rights and freedom. e.g. Saudi Arabia, Guantanamo Bay, China, Poland. In India, discrimination against lower caste. |
| Working of institutions | Setting up of effective administration and judiciary. e.g. Mexico, Myanmar and Chile. In India, control on custodial deaths. |
| Elections | To hold free and fair elections. e.g. Mexico, Chile, Pakistan, Poland. In India, taking measures to check rigging of elections. |
| Federalism, decentralization | To establish democratic institutions like administration and judiciary at local levels. e.g. Yugoslavia, Ghana, Belgium. In India, providing more power and resources to the local governments. |
| Accommodation of diversity | To resolve social diversified issues based on ethnicity, linguistic groups, etc. e.g. Ireland, Yugoslavia, Belgium, Sri Lanka. In India, conflicts due to caste and communal differences pose a challenge to democracy. |
| Political Organisation | To democratise organisations in countries. e.g. Ghana, Ireland, Saudi Arabia, Myanmar. In India, corruption of political parties is a challenge. |
| Any other category – Religious equality | To establish religious equality in countries. e.g. Saudi Arabia, Mayanmar, Iran. In India, religious, social and economic discrimination of people belonging to lower castes exists |
Question 4: Let us group these again, this time by the nature of these challenges as per the classification suggested in the first section. For each of these categories, find at least one example from India as well.
Answer:
| Foundational Challenge | Poland, Myanmar, Pakistan, Iraq, Nepal, Chile, China, Saudi Arabia Example from India – Naxal problem and insurgency in North-Eastern states. |
| Challenge of Expansion | Ghana, Saudi Arabia, Yugoslavia, Sri Lanka, Ireland, Mexico, Iraq. Example from India – To grant more powers to local governments like municipal bodies and village panchayats. |
| Challenge of deepening | South Africa, Pakistan, Belgium, Bolivia, US, Guantanamo Bay. Example from India – To increase women representation in Parliament and state legislatures. |
Question 5: Now let us think only about India. Think of all the challenges that democracy faces in contemporary India. List those five that should be addressed first of all. The listing should be in order of priority, i.e, the challenge you find most important or pressing should be mentioned at number 1, and so on. Give one example of that challenge and your reasons for assigning it the priority.
Answer:
| Priority | Challenges to Democracy | Example | Reasons for Preference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Challenge of Deepening | Corruption among government officials | People lose faith in democracy, and weakens the functioning of democracy. |
| 2. | Challenge of Expansion | Women’s participation in the legislature | Women constitute of half of the population so should have a fair amount of participation in |
| 3. | Foundational Challenge | Delay in justice from courts | People lose faith in democracy and weaken the foundations of democracy. |
| 4. | Foundational Challenge | Inflation and increasing poverty | A large section of the population is affected by this problem |
| 5. | Challenge of Expansion | Poor literacy amongst women | A large part of our population is not being adequately educated, hence, it is underutilized affecting the development of the country. |
Question 6: Here are some challenges that require political reforms. Discuss these challenges in detail. Study the reform options offered here and give your preferred solution with reasons. Remember that none of the options offered here is ‘right’ or ‘wrong’. You can opt for a mix of more than one options, or come up with something that is not offered here. But you must give your solution in detail and offer reasons for your choice.
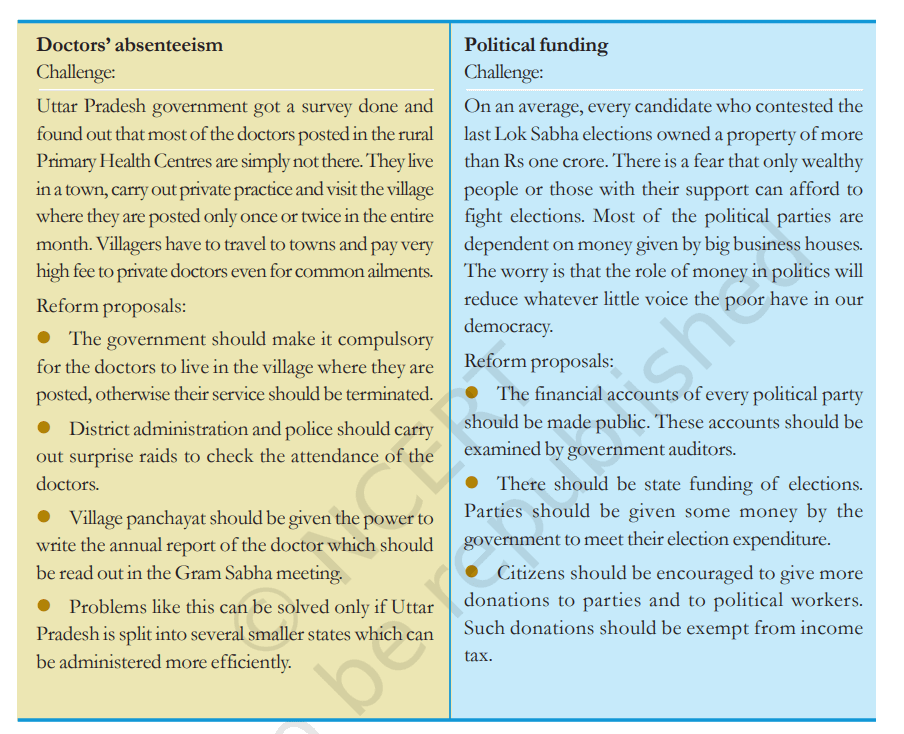
Answer:
(A) Doctor’s absenteeism :
Doctor’s absenteeism can be controlled by making some rules as part of their terms and conditions. It should be made compulsory for the doctors to live in the village of their posting. They should be debarred from doing private practice. They should be given some monetary incentives. These conditions must be strictly followed like surprise checks by the department should be made. The erring doctors should be punished by the department..
(B) Political funding :
To curb the flow of money in elections which distort the very meaning of democracy the first, two proposals i.e., auditing of accounts of the political parties and state funding are good because these reforms will bring transparency in the finances of the political parties. State funding will reduce the expenditure on elections. Role of money will be less and the poor candidates will get a chance to fight elections.
Question 7: Any other problem of your choice.
Answer:
Criminalisation of Politics Challenge:
Number of criminals in politics is increasing day by day. In 2019, 43 percent MPs have criminal records. People with criminal records get nomination to stand for the central and the state elections. This is a matter of concern about the outcome of the elections. Often such contestants get themselves elected either by rigging the votes or by distributing money to the people.
Reform proposals:
- People with serious criminal charges should be disqualified from contesting the elections.
- As suggested by Supreme court, fast courts should be set up for the trial of convicted MPs and MLAs.
- Any kind of monetary and material distribution to attract the voters should be completely prevented.
Question 8: Here is your space for writing your own definition of good democracy.
Answer: Bindhu’s definition of good democracy :
A good democracy is one in which the rulers elected by the people take major decisions under the framework of the Constitution of fulfill the wishes of the people, but if they do not withstand their expectations, people can call them back.
Features:
- If the representatives do not perform, people should have the right to call them back before time.
- People should be banned from contesting elections if found guilty of instances of breaking laws.
- Socio-economic matters should be taken care of equally to minimize economic inequality among citizens.
- A sufficient representation of the minority and disadvantaged classes should be provided in a democracy.
- The elected leaders should follow certain moral principles.
Question 9: Is it democratic for someone to dictate to us what a good democracy is?
Answer: No, it is not democratic for someone to dictate us what a good democracy is. Because democracy is a way of life how people utilise their voting rights to select political who rule them. In case if someone comes up with any good definition for democracy, it should be made public by authenticated persons like teachers, bureaucrats, lawyers. All people must get equal rights and opportunities in a democracy. Whether to accept that definition of democracy is to be left for public conscience.
.png)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.png)
0 comments:
Post a Comment